Singular-value-decomposition-based causal emergence for Gaussian iterative systems. Physical Review E, 2025, 112(5): 054225
Kaiwei Liu, Linli Pan, Zhipeng Wang, Mingzhe Yang, Bing Yuan, Jiang Zhang
This article proposes a pioneering CE quantification framework for Gaussian iterative systems (GIS), based on approximate dynamical reversibility derived from SVD of covariance matrices in forward and backward dynamics. The positive correlation between SVD-based and EI-based CE, along with the equivalence condition, are given analytically.
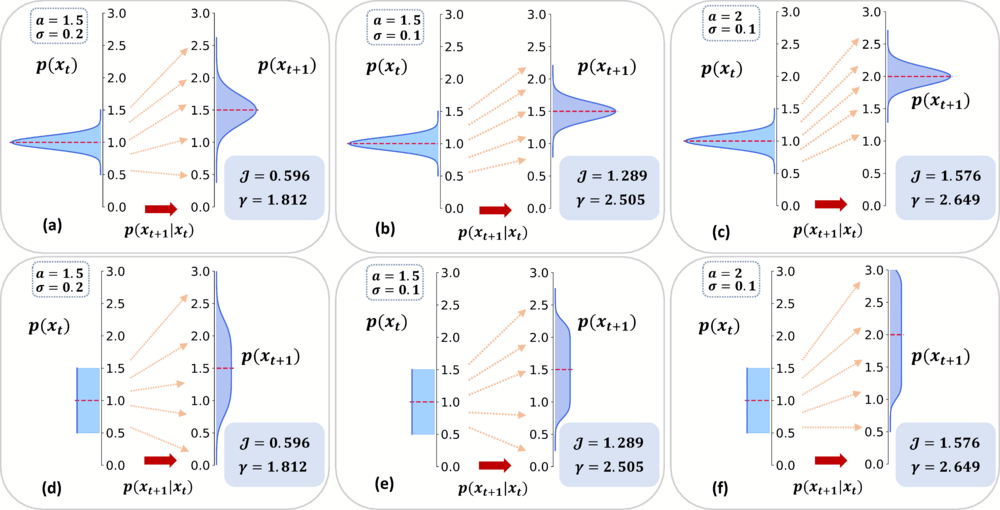
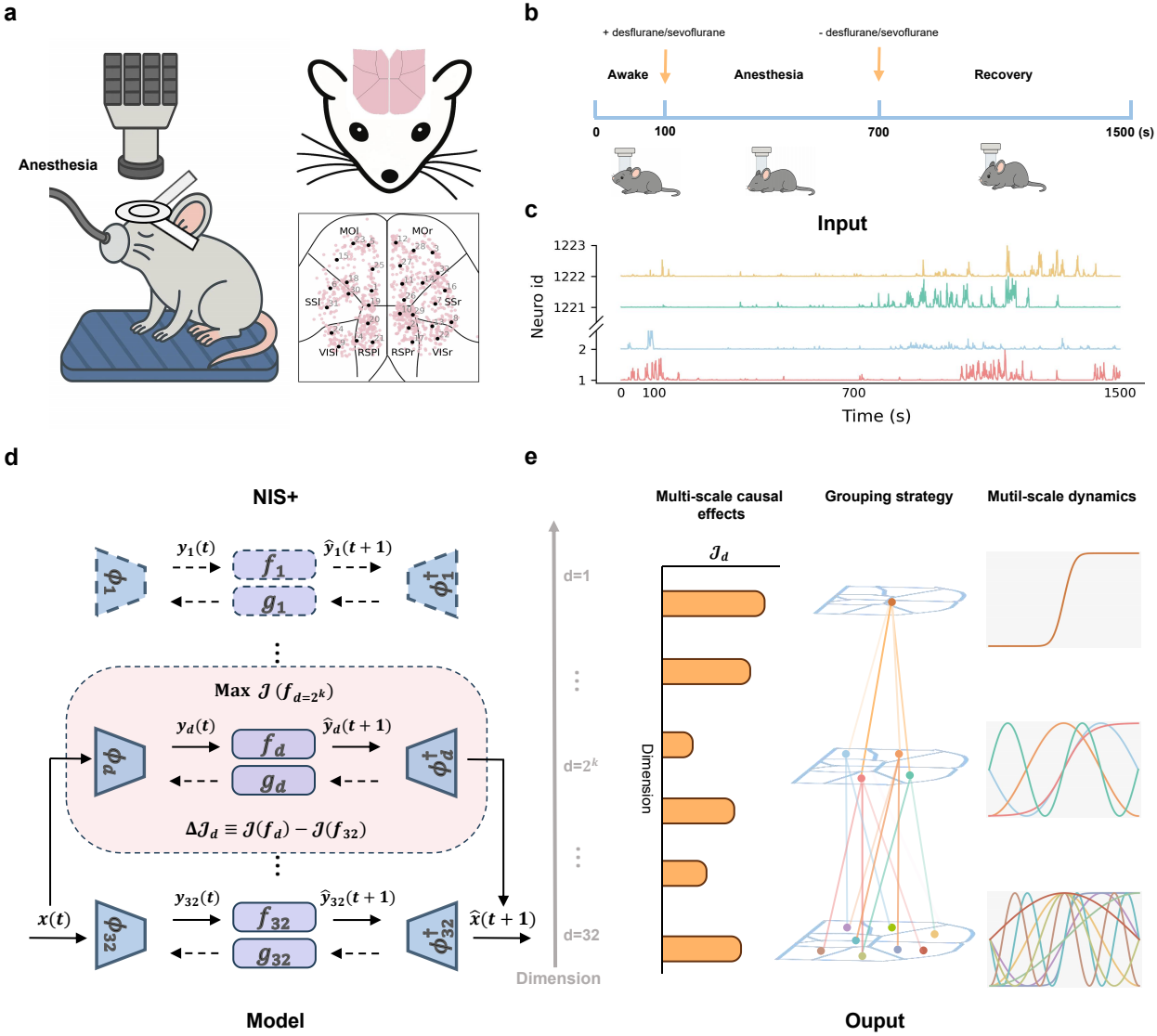
Causal Emergence of Consciousness through Learned Multiscale Neural Dynamics in Mice. arXiv:2509.10891, 2025
Zhipeng Wang, Yingqi Rong, Kaiwei Liu, Mingzhe Yang, Jiang Zhang, Jing He
Consciousness spans macroscopic experience and microscopic neuronal activity, yet linking these scales remains challenging. Prevailing theories, such as Integrated Information Theory, focus on a single scale, overlooking how causal power and its dynamics unfold across scales. Progress is constrained by scarce cross-scale data and difficulties in quantifying multiscale causality and dynamics. Here, we present a machine learning framework that infers multiscale causal variables and their dynamics from near–cellular–resolution calcium imaging in the mouse dorsal cortex.
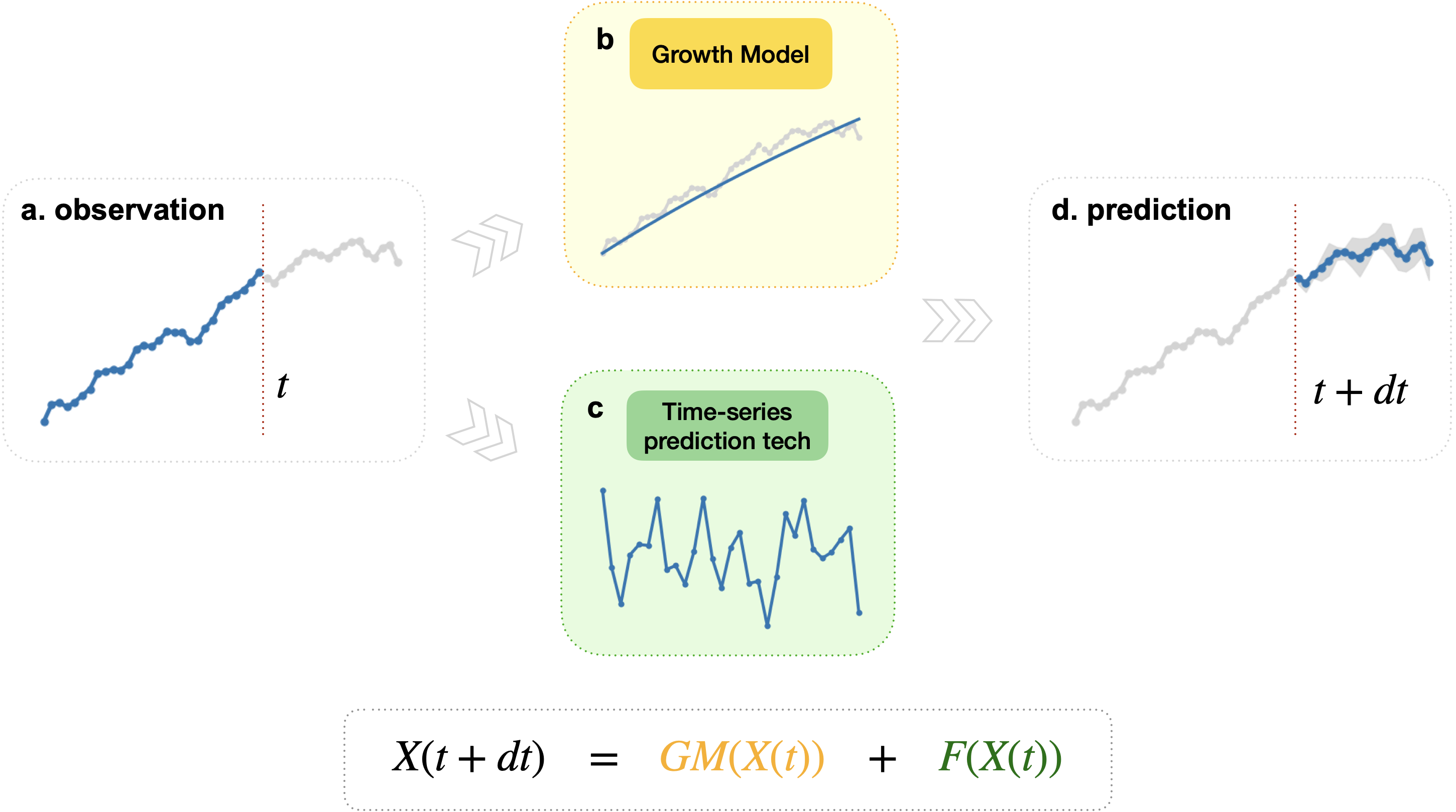
Predicting Company Growth by Econophysics informed Machine Learning. arXiv:2410.17587
Ruyi Tao, Kaiwei Liu, Jing Xu, Jiang Zhang
In this paper, we propose a machine learning-based prediction framework that incorporates an econophysics model for company growth. Our model captures both the intrinsic growth mechanisms of companies led by scaling laws and the fluctuations influenced by random factors and individual decisions, demonstrating superior predictive performance compared with methods that use time series techniques alone. Its advantages are more pronounced in long-range prediction tasks. By explicitly modeling the baseline growth and volatility components, our model is more interpretable.
Finding emergence in data by maximizing effective information. National Science Review, 2024, nwae279
Mingzhe Yang, Zhipeng Wang, Kaiwei Liu, Yingqi Rong, Bing Yuan, Jiang Zhang
Inspired by the theory of causal emergence (CE), this paper introduces a machine learning framework to learn macro-dynamics in an emergent latent space and quantify the degree of CE. The framework maximizes effective information, resulting in a macro-dynamics model with enhanced causal effects. Experimental results on simulated and real data demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed framework.
An Exact Theory of Causal Emergence for Linear Stochastic Iteration Systems. Entropy 2024, 26(8), 618
Kaiwei Liu, Bing Yuan, Jiang Zhang
In this study, we introduce an exact theoretic framework for causal emergence within linear stochastic iteration systems featuring continuous state spaces and Gaussian noise. Building upon this foundation, we derive an analytical expression for effective information across general dynamics and identify optimal linear coarse-graining strategies that maximize the degree of causal emergence when the dimension averaged uncertainty eliminated by coarse-graining has an upper bound.
Emergence and Causality in Complex Systems: A Survey of Causal Emergence and Related Quantitative Studies. Entropy 2024, 26(2), 108
Bing Yuan, Jiang Zhang, Aobo Lyu, Jiayun Wu, Zhipeng Wang, Mingzhe Yang, Kaiwei Liu, Muyun Mou, Peng Cui
This paper provides a comprehensive review of recent advancements in quantitative theories and applications of CE. It focuses on two primary challenges: quantifying CE and identifying it from data. The latter task requires the integration of machine learning and neural network techniques, establishing a significant link between causal emergence and machine learning. We highlight two problem categories: CE with machine learning and CE for machine learning, both of which emphasize the crucial role of effective information (EI) as a measure of causal emergence. The final section of this review explores potential applications and provides insights into future perspectives.

Expectation-maximizing network reconstruction and most applicable network types based on binary time series data. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena, 454 (2023): 133834
Kaiwei Liu, Xing Lü, Fei Gao, Jiang Zhang
In this paper, focusing on the differences in the effectiveness of simplicial complexes reconstruction after the same number of iterations, we innovatively propose that simplex reconstruction based on maximum likelihood estimation is more suitable for small-world networks and three indicators to judge the structural similarity between a network and a small-world network are given.
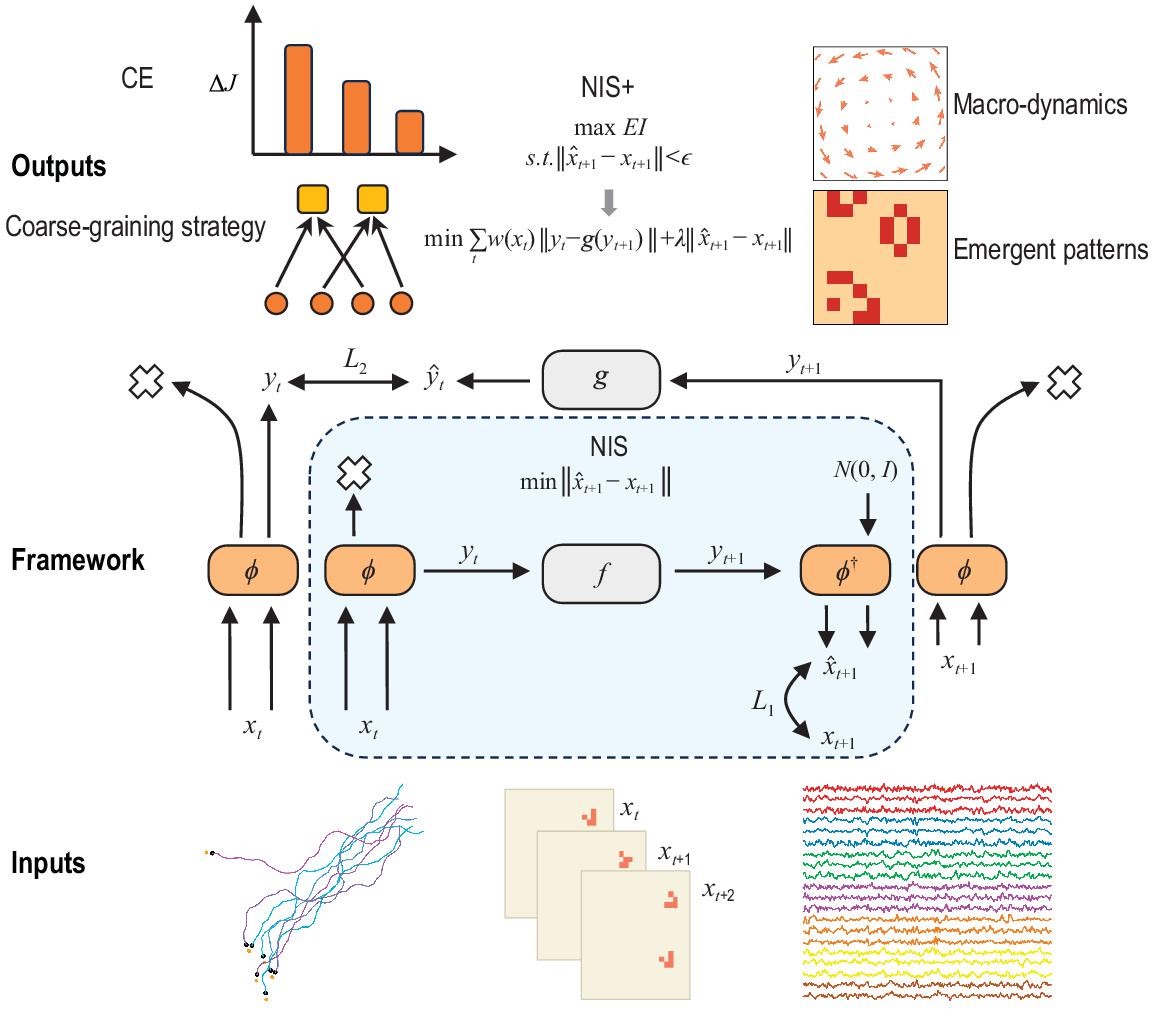
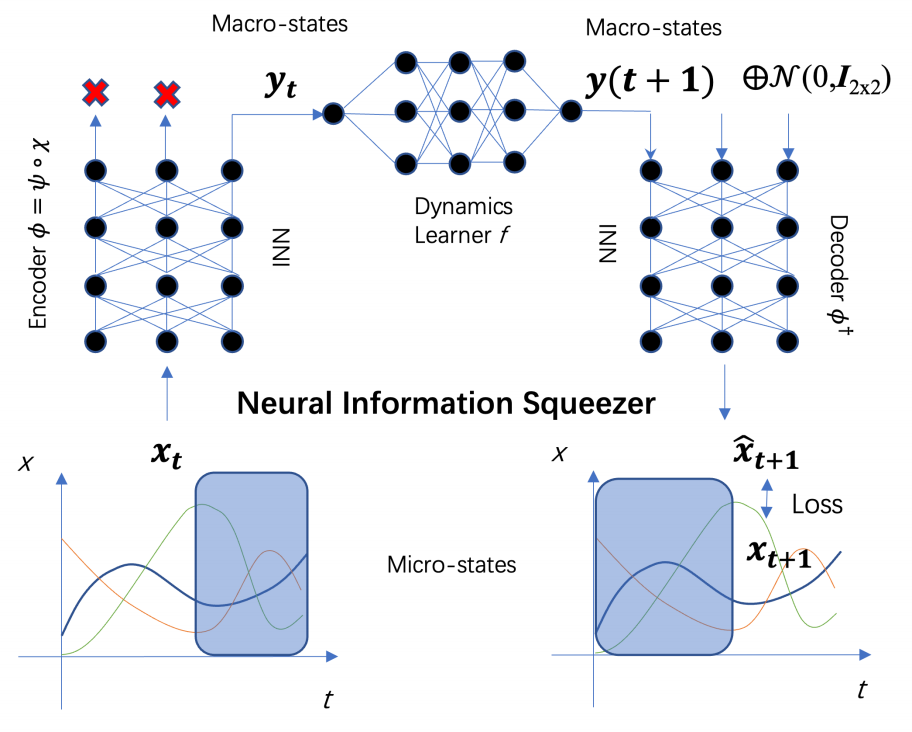
Neural Information Squeezer for Causal Emergence. Entropy 2023, 25(1), 26
Jiang Zhang, Kaiwei Liu
This paper proposes a general machine learning framework called Neural Information Squeezer to automatically extract the effective coarse-graining strategy and the macro-level dynamics, as well as identify causal emergence directly from time series data. By using invertible neural network, we can decompose any coarse-graining strategy into two separate procedures: information conversion and information discarding.
Bayesian and E-Bayesian Estimations of Bathtub-Shaped Distribution under Generalized Type-I Hybrid Censoring. Entropy, 2021, 23(8): 934
Yuxuan Zhang , Kaiwei Liu, Wenhao Gui
For the purpose of improving the statistical efficiency of estimators in life-testing experiments, generalized Type-I hybrid censoring has lately been implemented by guaranteeing that experiments only terminate after a certain number of failures appear. With the wide applications of bathtub-shaped distribution in engineering areas and the recently introduced generalized Type-I hybrid censoring scheme, considering that there is no work coalescing this certain type of censoring model with a bathtub-shaped distribution, we consider the parameter inference under generalized Type-I hybrid censoring.
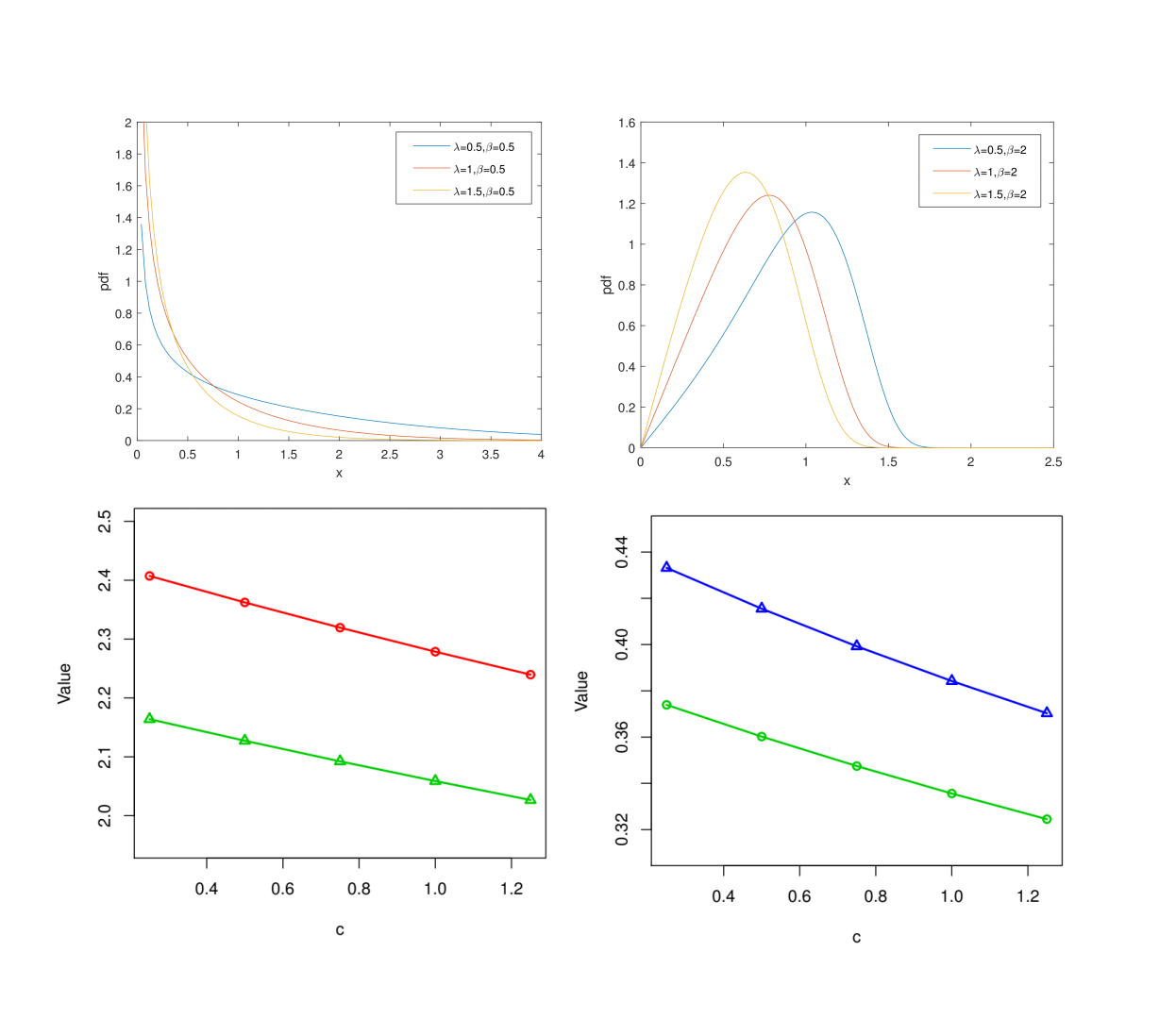
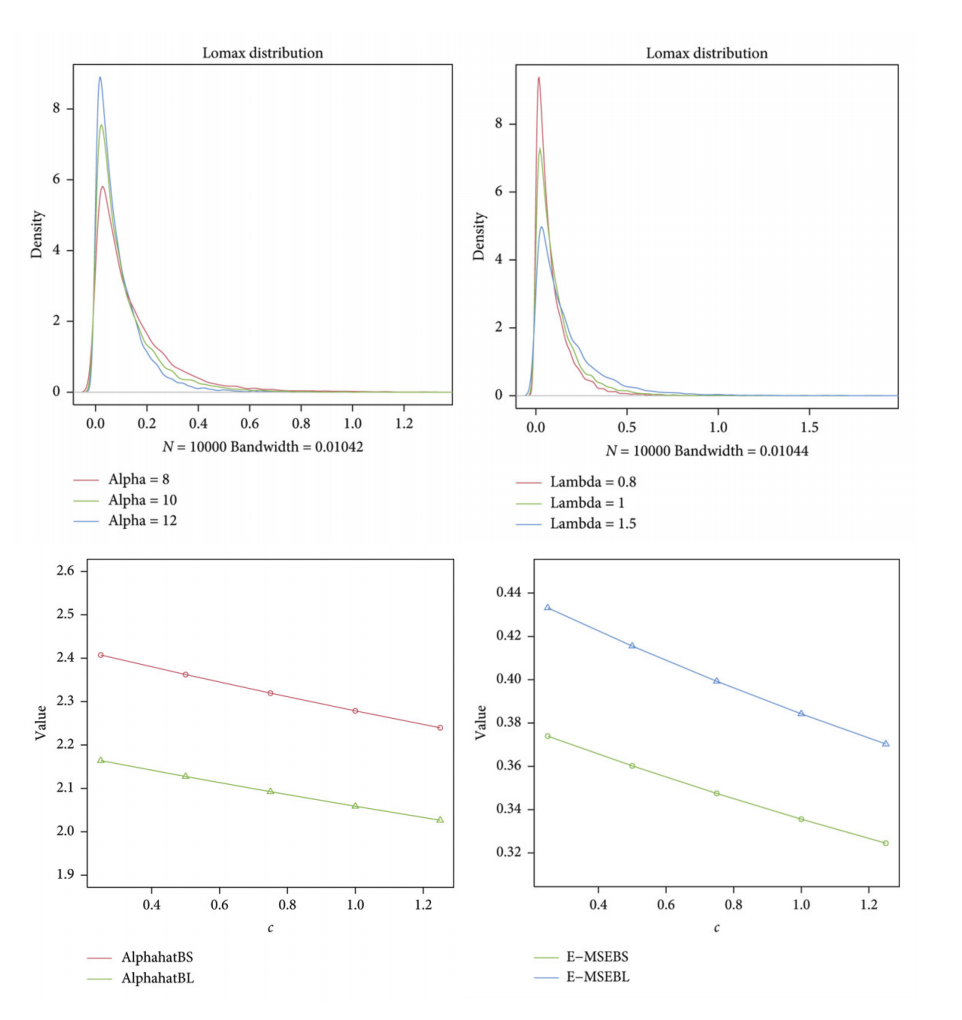
The E-Bayesian Estimation for Lomax Distribution Based on Generalized Type-I Hybrid Censoring Scheme. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2021, 2021: 19
Kaiwei Liu, Yuxuan Zhang
This article studies the E-Bayesian estimation of the unknown parameter of Lomax distribution based on generalized Type-I hybrid censoring. Under square error loss and LINEX loss functions, we get the E-Bayesian estimation and compare its effectiveness with Bayesian estimation. To measure the error of E-Bayesian estimation, the expectation of mean square error (E-MSE) is introduced. With Markov chain Monte Carlo technology, E-Bayesian estimations are computed.